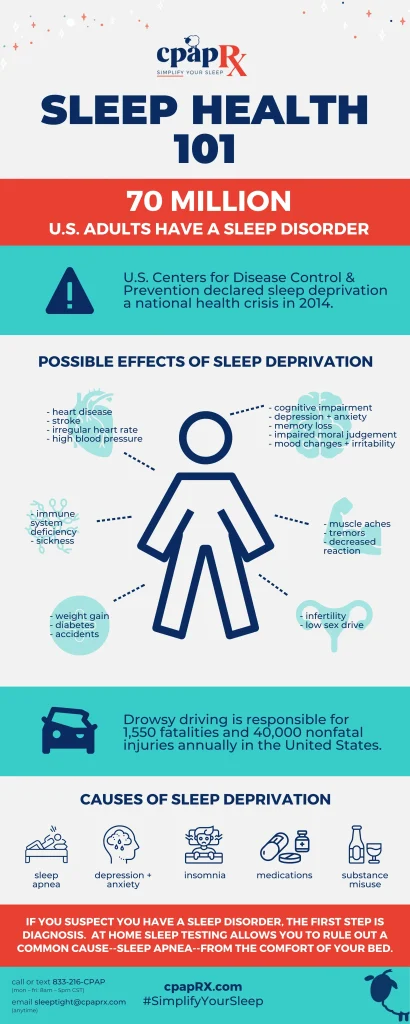
Sleep health is a foundational pillar of overall wellness, quietly powering both your body and brain. When you prioritize consistent, restorative rest, you may notice better immune resilience, sharper memory, and steadier mood throughout the day. This is why understanding sleep health benefits and adopting practical habits can transform daily performance and long-term vitality. Sleep quality, circadian rhythm and health, and tips for better sleep all point to the same core idea: restful nights support a healthier, more resilient you. By framing your nighttime routines around evidence-based strategies, you can safeguard restful nights and daily vitality.
Viewed through an LSI lens, the topic translates into rest quality and overnight recovery that power daytime function. A well-tuned sleep-wake cycle, guided by circadian rhythm alignment, supports immune resilience, learning, and mood. Practices framed as sleep hygiene, consistent bedtimes, and appropriate light exposure are common LSI-related terms that help people relate to the idea. Rather than focusing on hours alone, you’re looking at circadian biology, nighttime restoration, and the body’s clock guiding energy and repair. In practical terms, this means creating regular routines, limiting evening stimulation, and prioritizing quality rest to boost daily performance.
Sleep Health Essentials: How Rest Powers Your Body and Brain Daily
Sleep health is more than hours in bed; it shapes immunity, memory, mood, and performance. Grounded in sleep quality, duration, and regularity, healthy sleep supports circadian rhythm and health, promoting metabolic balance and hormonal harmony. By focusing on sleep health benefits, you set a foundation for daily vitality.
During a typical night, you cycle through NREM and REM stages, enabling physical repair, learning, and emotional regulation. This nighttime work underpins cognitive function, attention, and long-term brain health. Prioritizing sleep quality and a consistent wake-sleep schedule strengthens circadian rhythm, reduces daytime fatigue, and supports better decision-making.
Sleep Health and Immunity: Strengthen Your Body with Quality Rest
Sleep and immune system are closely linked. Sufficient sleep boosts antibody production and immune cell activity, while chronic sleep debt can blunt defenses and slow recovery. Protecting sleep health helps your body defend against infections and respond to vaccines, illustrating sleep health benefits in everyday life.
To optimize, anchor a predictable sleep schedule, manage light exposure to cue your circadian rhythm, and create a sleep-friendly environment. Practical steps—regular physical activity, mindful caffeine use, and a calming pre-sleep routine—are part of tips for better sleep that consistently improve sleep quality and immune function. In short, aligning your circadian rhythm and health through consistent rest yields tangible daytime benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the sleep health benefits for the immune system and daily performance?
Sleep health benefits include a stronger immune system, sharper memory, and steadier mood. Sleep supports the sleep and immune system by promoting antibody production and immune cell activity, while chronic sleep deprivation can blunt immune responses. To maximize these benefits, aim for 7–9 hours of sleep, keep a consistent schedule, optimize your sleep environment, manage stress, and limit caffeine, especially later in the day.
Which tips for better sleep most effectively improve sleep quality and support circadian rhythm and health?
Tips for better sleep that boost sleep quality and circadian rhythm and health include: keep a consistent bed and wake time to reinforce your circadian rhythm; create a cool, dark, quiet sleep environment; get bright light in the morning; limit caffeine and alcohol, especially in the hours before bed; establish a wind‑down routine and relax before sleep; avoid heavy meals close to bedtime; and stay physically active during the day. If sleep concerns persist, consult a healthcare professional.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What Sleep Health Is |
|
| The Science Behind Sleep Health (NREM/REM) |
|
| Core Benefits |
|
| Circadian Rhythm |
|
| Sleep Duration vs. Sleep Quality |
|
| Practical Ways to Improve Sleep |
|
| Sleep Quality and Cognitive Function |
|
| Sleep Duration, Quality, and Immune Function |
|
| Common Myths Debunked |
|
| Putting Sleep Health into Practice: Personal Plan |
|
Summary
Sleep health is a dynamic, multidimensional pillar of wellness that influences nearly every aspect of daily life. By prioritizing consistent sleep duration, optimizing sleep quality, and supporting circadian rhythm, you empower your immune system, sharpen memory and cognitive function, stabilize mood, and enhance physical performance. The benefits aren’t reserved for athletes or night owls; they’re accessible to anyone who commits to a regular, restorative sleep routine. Start with small, actionable steps today, track your progress, and make sleep health a central habit of a healthier life.